LiFePO4 Battery Cells in Different Shapes
Cylinder Cell
Cylinder cell is the most traditional and the oldest, but also the safest technology. Because of the round shape, the internal pressure is equally shared on the surface, and the heat dissipation is better. Due to the mature automated production line and technology, cylinder cell is much safer, more efficient, and more consistent.
A cylinder cell is quite small, an 18650 is generally around 2200mAh. Mostly, the capacity is calculated in mAh. Other size models are 18650, 26650, 32650, and so on.
It is always used in small mobile applications. Such as power banks, drones, flashlights, electric toys, electric tools, digital electronics, and other small portable power systems.
Tesla chose a 21700 cylinder cell for the Model 3. It’s a pretty large battery system, with a great number of individual cylinder cells. The huge battery system requires an extremely high level of consistency, excellent BMS performance management, and a very well-designed heat dissipation system.
In most cases, it is not recommended to build a large battery system with cylinder cells.
Prismatic cells are more suited because the required quantity of the battery cells will be much smaller.
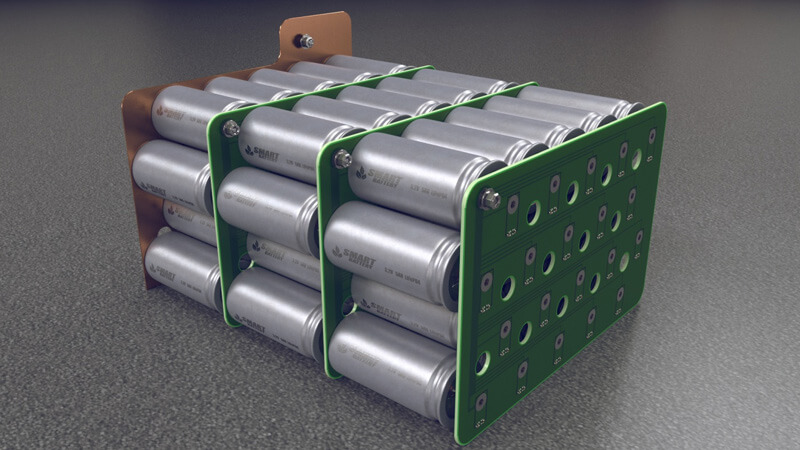
Prismatic Cell
Prismatic cells are popular because of their high capacity and square shape. Anyone can easily connect 4 cells in series to create a 12V battery pack. For example, a 12V100Ah, or the currently popular EVE 3.2V280Ah, can build a 12.8V280Ah battery pack. Or, you can even make a 48V280Ah battery system with 16 cells.
The battery pack of prismatic LiFePO4 cells will be more stable because there are fewer cells in the pack, and the BMS can independently work for each cell.
Prismatic cells are widely used in energy storage applications. As the energy density of LiFePO4 is not as high as NMC cells, there is a weakness in mobile applications. But in stationary energy storage systems, it is not a key factor.
Moreover, in power applications, due to the outstanding cycle life of LiFePO4 batteries, more and more companies choose LiFePO4 battery cells in low-speed vehicles, AGVs, cleaning machines, and the current EVs.

Pouch Cell
Pouch cell, cylinder cell, and prismatic cell, there is very little difference between the positive and negative electrode materials and separators. The biggest difference is the packaging material.
The main feature of the pouch cells is the aluminum-plastic shell instead of metal, which means it is not that heavy and has a higher energy density than the above two types. But relatively, it is easier to be damaged, not that strong in impact resistance. If we make it into a battery pack, the case protection must be good.
The aluminum-plastic film packaging is flexible. When a safety problem appears, the pouch cell will bulge and break, but it will not explode or get on fire.
Shapes of pouch cells can be customized. Shapes can be tailor-made to maximize battery compartment space and increase battery capacity.
It is used in smartphones, drones, wearable devices, the automotive industry, the military field, etc.

LiFePO4 Battery Cells in Different Current Grades
1C – Energy Storage
Most of the energy storage LiFePO4 cells have a benchmark charge/discharge rate of 1C. Meaning it can be discharged for one hour at 1C current. In comparison, lead-acid batteries can only be discharged at 1C for 30 minutes or less.
Due to the BMS protection of LiFePO4 battery, in the case of current over 1C, the BMS will cut off the circuit to protect the battery cells. So most of the energy storage LiFePO4 batteries are designed not to discharge above 1C! This is very different from lead-acid batteries, please pay attention.
2C/3C – Higher Power
2C and 3C cells are better in higher current performance. They can drive more power with less room and capacity.
5C and higher, EV grade cells
5C and higher battery cells are mostly used in UPS and Electric Vehicles.
The main reasons are high instant power and charge speed demands. Not only do the battery cells need to be capable of high current, but also the BMS, connection joints, and internal cables need to be capable of this high current as well.
Different Applications and Design Purposes
Monoblock LiFePO4 Battery
Lead Acid Battery Drop-In Type | Small and Medium Battery System
Energy storage type
MonoBlock LiFePO4 Battery is designed to replace the original lead-acid battery. However, due to the BMS feature, these batteries are not appropriate for large-scale battery systems.
It is better to use it individually. If connected in series and parallel, it is not recommended to use too many units in series and parallel.
The main applications are small and medium solar storage systems, RVs, ships, etc.
Recommended maximum capacity is 48V, and 15kWh of power.
Especially, avoid the BAD connection while connected in parallel.
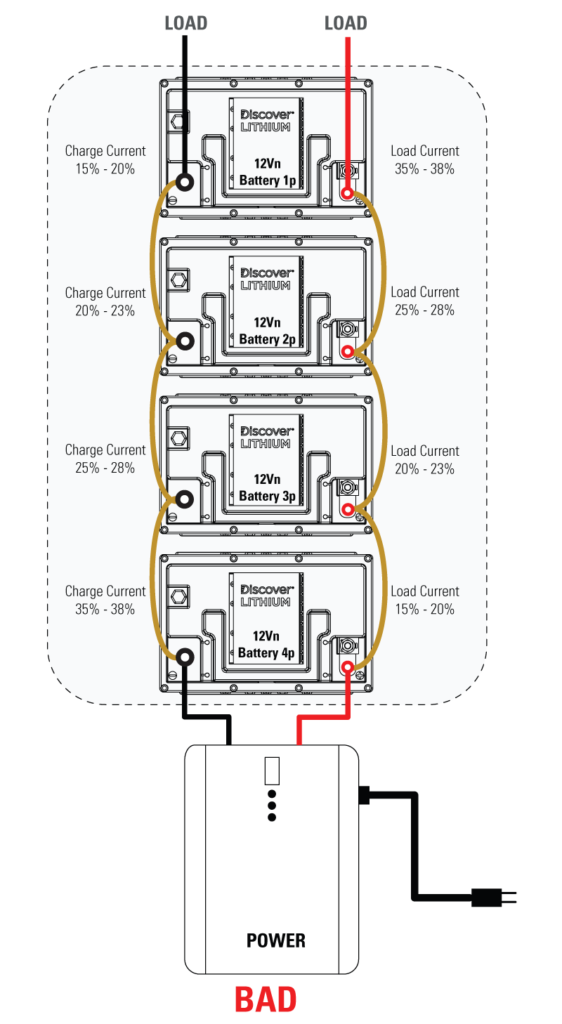
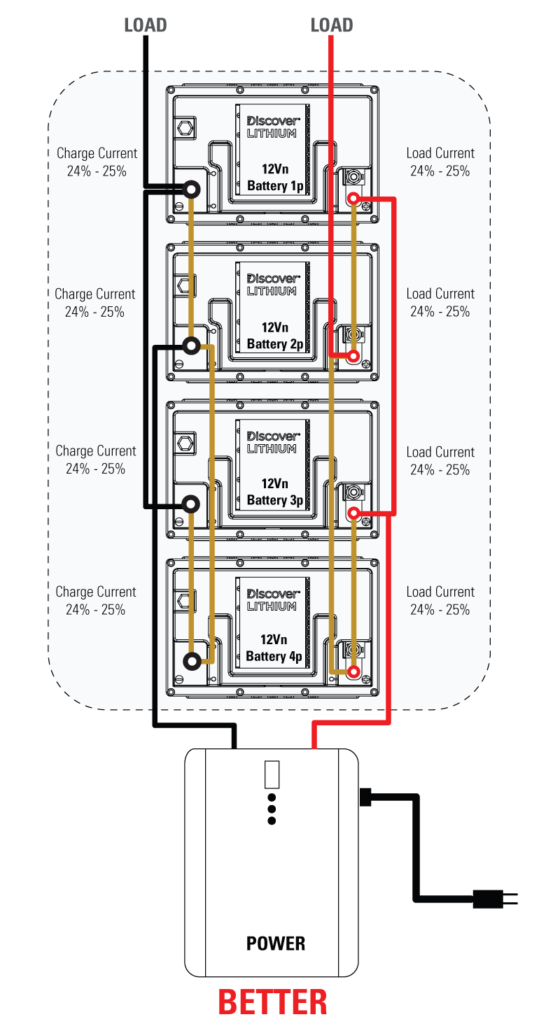
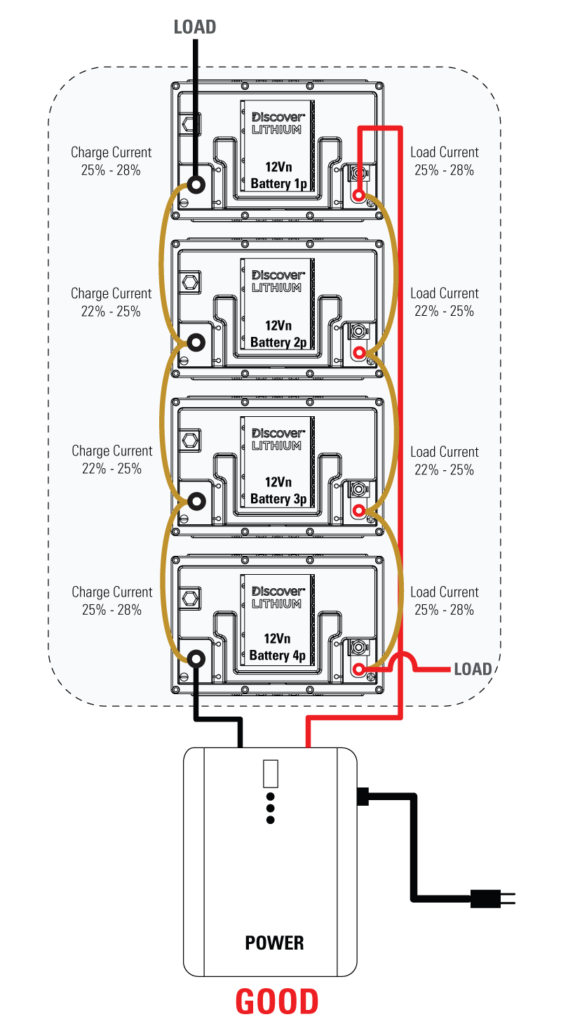
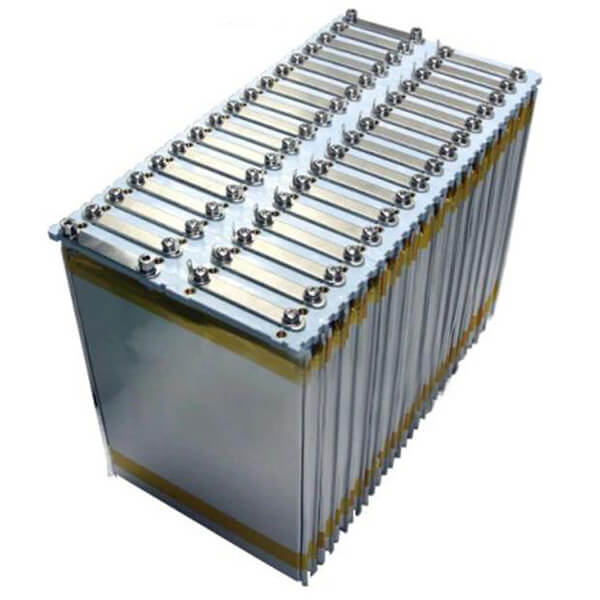
Modular LiFePO4 Battery
Scalable, 5kWh, 10kWh, 50kWh, and higher
Energy storage type
Modular LiFePO4 batteries are built with communication module to support inter-battery balancing and inverter interaction.
10 units of 48V(51.2V)100Ah can be connected in parallel as a group, achieving a capacity of 48V(51.2V)1000Ah, over 50kWh.
More groups can be connected in series and parallel to achieve a huge amount of capacity requirements through PCS(Power Control Unit).
Residential LiFePO4 Battery
Home Energy Storage System(HESS)
Energy storage type
Residential LiFePO4 Battery is mainly designed for home energy storage systems. Good-looking, home-style designs, can be integrated with household decoration in harmony.
The performance is similar to Modular LiFePO4 Battery. They can also be connected in parallel to achieve higher capacity.
High Rate LiFePO4 Battery
Power Type
Motors require higher currents from the battery.
1C is always enough to run low-speed vehicles. But if for some reason, a smaller battery compartment or a lower budget, then a higher rate battery can be of help.
Specialty Battery
Specialty battery is used in extreme environments, such as extreme cold, hot and humid.
Specialty battery has a better performance in low temperature, high temperature, and airtight.










One Response